Article Details
Completion Time: 30 min
Difficulty: Beginner
Subject: Computer Network Technologies and services
This article is about MPLS (Multi Protocol Label Switching). We will first learn what is MPLS. we will see how it works and finally some of its applications.
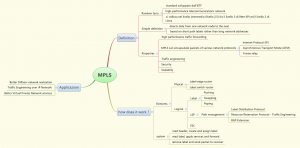
1. What is MPLS ?
MPLS stand for Multi Protocol Label Switching. Let’s begin with some random facts about MPLS:
MPLS is a standard developed by IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). It is high performance telecommunication network.
MPLS works between the layer 2 (Link) and the layer 3 (Network) of the ISO/OSI model.
Now a simple definition: MPLS is a standards-based technology used to speed up the delivery of network packets over multiple protocols.
MPLS have many properties:
- High performance
MPLS is faster in data forwarding and packet management inside the node. The complex operation on packet are done at the edge of the network
- Multi Protocol
- Traffic engineering
- Securtiy
- Scalability
- Quality of Service management
MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols: IP (Internet Protocol), ATM (Asynchronous Transport Mode), Frame Relay
MPLS create network path with optimization of resources use.
In MPLS, routing is based on label who are assigned by an internal protocol in the network so not visible.
an MPLS network can grow without high cost on hardware and software.
MPLS use a connection-oriented transfer mode who is the base to give some prefixed quality level services.
2. How does MPLS work ?
To understand how MPLS works, we will see in details all its elements.
Logical Elements
Label
Label is a fixed lenght identificator of packet in the network.
Forwarding equivalence class (FEC)
FEC is i class to identify the class of a packet in the network. It’s associated to the packet label.
Label Switched Path (LSP)
LSP is a path inside an MPLS network created by some protocol (Label Distribution Protocol, Resource Reservation Protocol – Traffic Engineering, BGP Extension).
Physical Elements
Label edge router (LER)
LER is a Router locate in the perimetrical zone of the MPLS network.It can be ingress router or egress router. It read packet header in entrance to determinate the FEC and assign a Label to the packet. It also remove label for outgoing packet.
Label switch router (LSR)
LER is a Router locate in the internal zone of the MPLS network. It read label, apply some services and forward the packet to the next router.
So now we know the elements, how MPLS really works ?
When an unlabeled packet enters the ingress router(LER) and needs to be passed on to an MPLS path (LSP), the router first determines the forwarding equivalence class (FEC) for the packet and then inserts one or more labels in the packet’s newly created MPLS header. The packet is then passed on to the next hop router (LSR) for this path. When the packet arrive to an egress router, this one remove the label and send the packet to the receiver.
3. MPLS Applications
- Diffserv Network over MPLS
- IP Network over MPLS
- MPLS-based VPN
A Diffserv network over MPLS will be more efficient. The analogies between the 2 architectures make the collaboration simpler.
In this way the network can use MPLS Traffic engineering techniques.
The VPN(Virtual private Network) built on top of an MPLS network, will provided services in an efficient way.
5. Links and Literature
- Wikipedia article
- internet voice article
- Lecture Notes of Rome University “La Sapienza”
- Lecture Notes of Genova University from Prof. Raffaele Bolla
7. Thank you
Support my challenge, support my blog. Please Share this article if you found it useful. Thank you.